Reactions involving carbanions
Carboxylic acids are acidic due to the stability of the resonance hybrid carbanion.
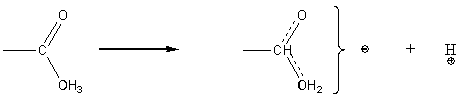
Hydrogens attached to carbon atoms immediately adjacent to a carbonyl carbon (a hydrogens) are acidic for the same reason.
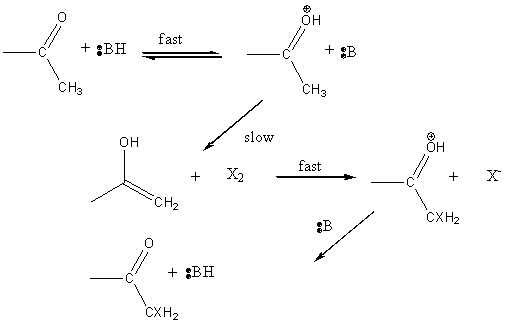
Halogenation of ketones
Base promoted
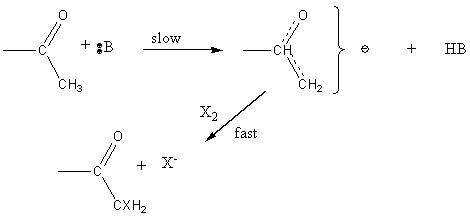
Acid catalyzed
In contrast, acid catalyzed halogenation does not involve a carbanion but rather a carbonium ion. not involve a carbanion but rather a carbonium ion.
The Aldol condensation
The carbonyl carbon is subject to nucleophillic attack due to the ability of the intermediate to accommodate a negative charge.
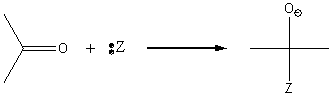
Carbonyl compounds under basic conditions form a carbanion with nucleophillic character.
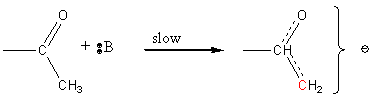
This nucleophile can now add to the carbonyl carbon to form a b hydroxy carbonyl compound.
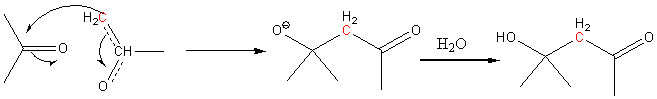
So, acetone gives 4-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-pentanone also known as diacetone alcohol.
The Aldol product can undergo dehydration.
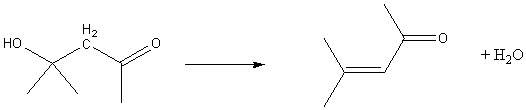
So, diacetone alcohol gives 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one (mesityl oxide).
The Wittig Reaction
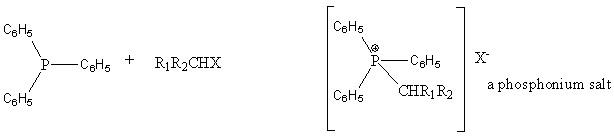
Triphenylphosphine reacts with alkyl halides to form an ylide.
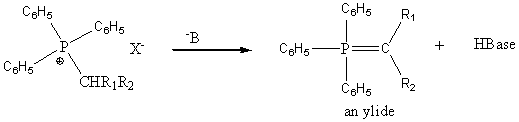
The ylide can be represented by the following two resonance structures and has a carbanion like character.
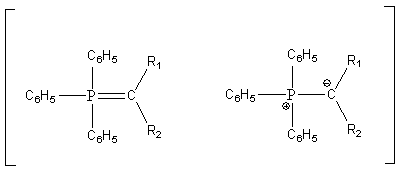
The ylide can react as a nucleophile towards a carbonyl carbon to form a betaine.
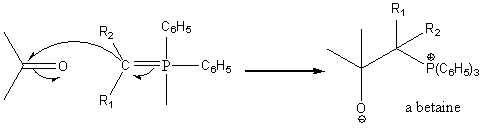
The betaine goes on to form a new compound where the original =O group has been replaced by a = CR1R2 group.
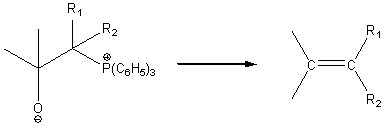
The Claisen condensation
In the presence of an alkoxide ion the a hydrogen of a carboxylic acid ester is abstracted to form a carbanion.
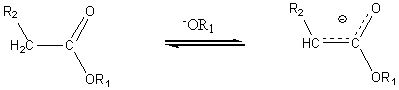
This carbanion is a nucleophile which can in turn attack the carbonyl carbon of the same or different carboxylic acid ester
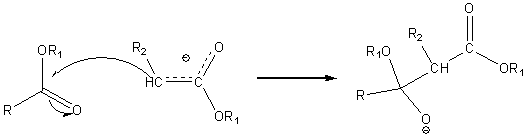
The resulting intermediate loses an alkoxide ion. In the reaction mixture (strongly basic due to the presence of the alkoxide ion) the product is present as the following very stable carbanion.
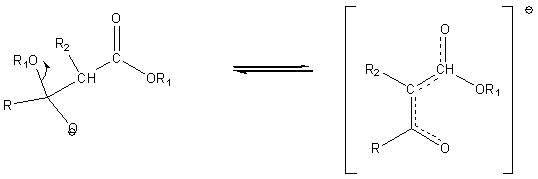
Upon acidification a b-keto ester is formed.
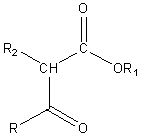
Acetoacetic ester is one important b-keto ester.
The Reformatsky reaction
In this reaction Zinc is reacted with an a bromo ester to form a nucleophile
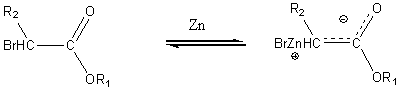
This intermediate can then react with the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde or ketone to form an intermediate which upon acidification yields a b-hydroxy ester.
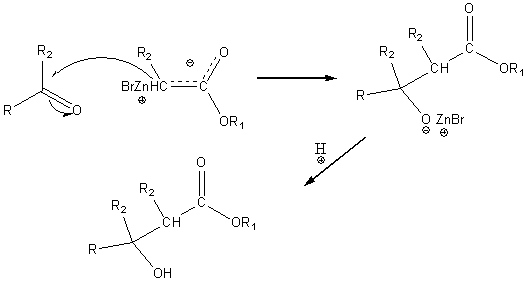
The reaction product can be dehydrated to form a, b unsaturated esters which can be hydrogenated and then hydrolyzed to form carboxylic acids.
Malonic ester synthesis of carboxylic acids
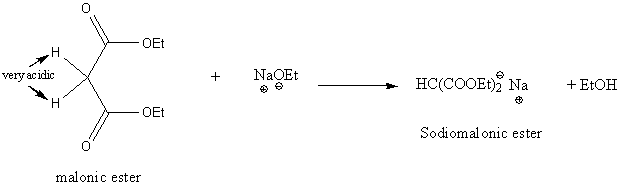
Reaction of sodiomalonic ester with an alkyl halide gives an alkylmalonic ester.
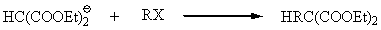
The alkylmalonic ester can be further reacted with sodium ethoxide and the resulting salt reacted with an alkyl halide to form a dialkylmalonic ester.
The esters can be hydrolyzed to the malonic acids. Acid and heat forms a substituted acetic acid.
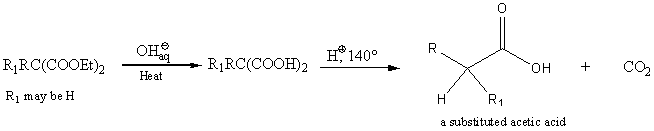
Acetoacetic ester synthesis of ketones
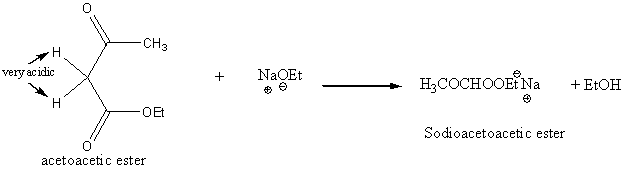
Reaction of sodioacetoacetic ester with an alkyl halide gives an alkylacetoacetic ester (aka an ethyl alkylacetoacetate).

The alkylacetoacetic ester can be further reacted with sodium ethoxide and the resulting salt reacted with an alkyl halide to form a dialkylacetoacetic ester.
The esters can be hydrolyzed to the corresponding acids acids. Acid and heat (sometimes not necessary) causes decarboxylation to form ketones
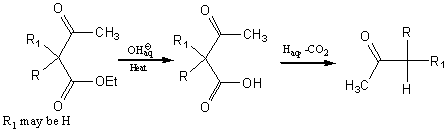
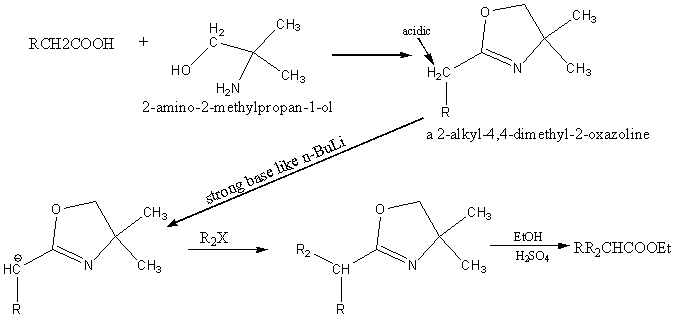
Synthesis of acids and esters via 2-oxazolines
A protective group for the carboxyl functionality.
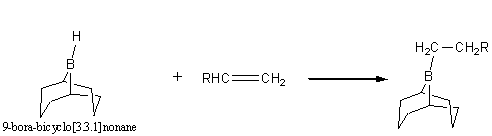
Organoborane synthesis of acids and ketones
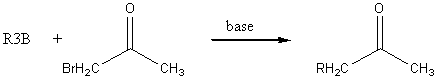
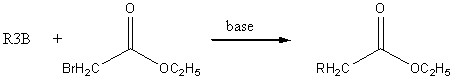
The best base is
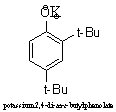
A good alkylborane can be prepared by the following scheme:
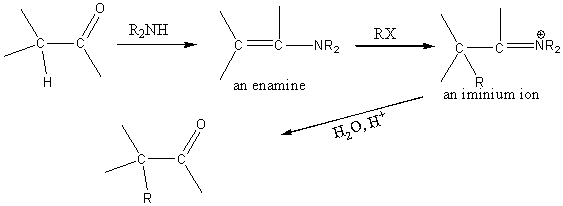
Alkylation of carbonyl compounds via enamines